Wastewater levels of SARS-CoV-2 are still LOW in most places in America according to both the CDC and WastewaterSCAN. As of 11/15/24, JP Weiland predicts that there are presently 185,000 new COVID infections per day in the US and that about 1 in every 180 people is currently infected. Mike Hoerger predicts a large increase in cases by December, but JP Weiland said that since COVID infections have decreased again this week, it looks less likely that we will reach as high a winter wave as last year. Still, it is a great time to get your updated COVID vaccine and the flu shot in order to be better protected when visiting friends and family for Thanksgiving and other winter holidays.
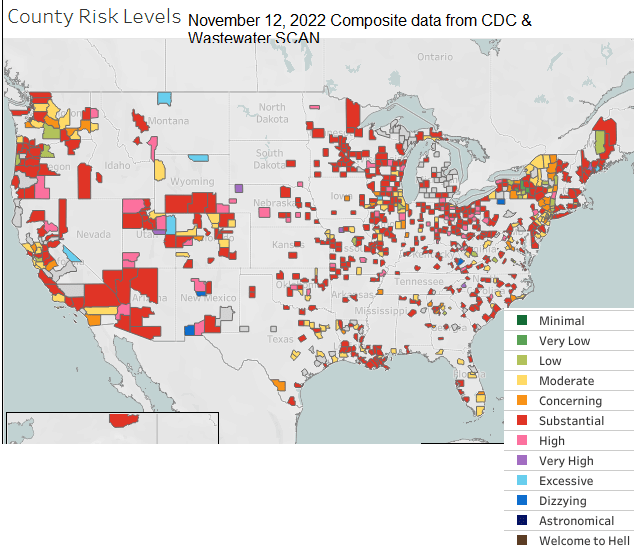
We can see on the composite wastewater chart from Sara Anne Willette using data from both the CDC and from WastwaterSCAN that there are more hotspots this week, seen as light blue and blue on the map below. Using data from both sources allows us to see data from most states.
SARS-CoV-2 Variants
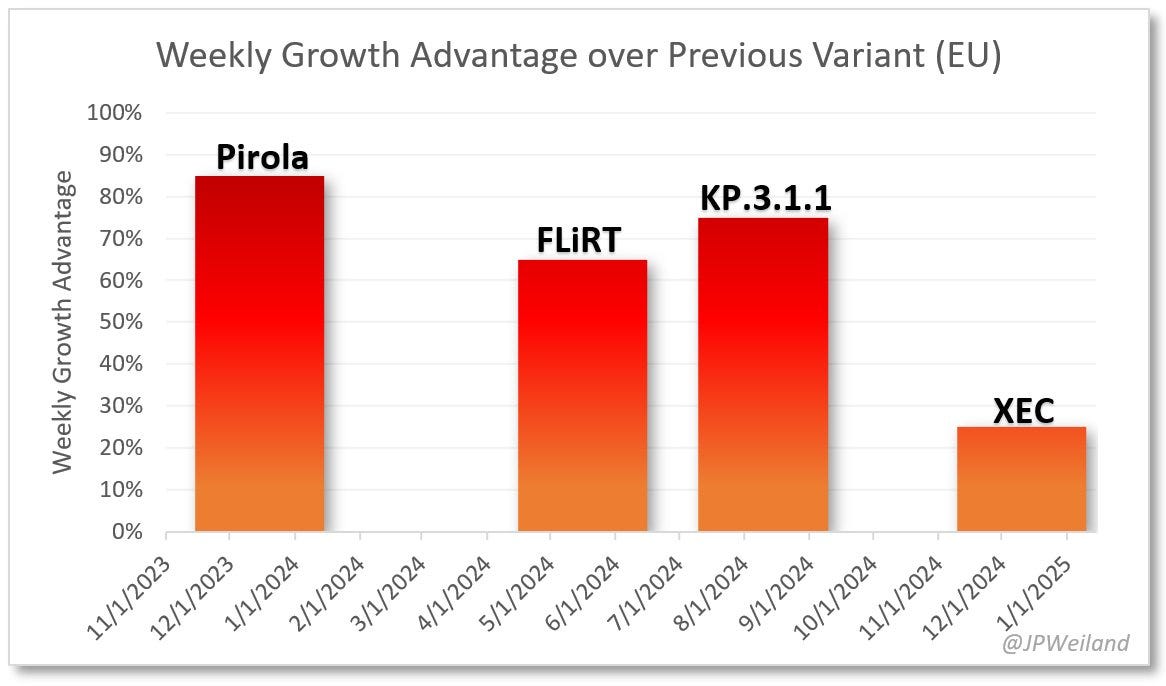
Variant data is only updated every 2 weeks by the CDC now. Last week, we saw that KP.3.1.1 decreased to 52% of COVID cases and that XEC was at 28% of cases. JP Weiland posted that last winter’s wave was caused by Pirola (BA.2.86) which caused a high wave and that this summer’s big wave was caused by the FLiRT mutations and then KP.3.1.1, but XEC does not show the same weekly growth advantage and therefore it is not expected to cause as big of a winter COVID wave. With indoor festivities during the holidays, COVID cases are expected to go up, just not as much as last year.
From: https://x.com/JPWeiland/status/1856477994090459219
Seniors
By November 2nd, 37.6% of Americans ages 65 and older had gotten an updated 2024-2025 COVID vaccine, compared to 22.6% the same week in 2023. 55.3% of seniors have gotten their flu shot which is similar to last year.
Pediatrics
In a study of 212,655 children and teens hospitalized for respiratory infection in 2020 to 2021, COVID infection caused a higher risk of myocarditis and heart block than influenza or RSV. There were no differences in tachyarrhythmias, cardiac arrest,or in-hospital mortality however. The authors summarized that children and teens hospitalized for COVID are at higher risk for cardiovascular complications compared to RSV or flu and it is important to limit the spread of infection.
COVID infection during pregnancy has been associated with an increase in neurodevelopmental disorders in the child, but mechanisms were previously unknown. A study from China shows that maternal COVID infection changes the number of CD4 T cells and affects gene expression. This leads to changes in astrocytes, endothelial cells, and excitatory neurons in the fetus which is associated with an increased risk of neurodevelopmental disorders in the affected newborns.
The California Department of Public Health (CDPH) has updated their recommendations for air quality in schools. In order “to prevent the spread of respiratory infections and decrease absenteeism, CDPH recommends providing a minimum of at least 5 air changes per hour or 30 cfm/occupant of equivalent clean airflow, whichever is greater, in occupied classroom environments. This goal can be achieved through a combination of ventilation with outdoor air and filtration using HVAC filters and/or portable air cleaners.”
Vaccines
The FDA removed the clinical hold on Novavax’s COVID-Influenza combination vaccine Phase 3 trial. A trial participant had noted a motor neuropathy, but further investigation showed that this was due to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and not the vaccine.
Antiviral treatments
David Ho's lab from Columbia University made their own Pemivibart (Pemgarda) monoclonal antibody to test against SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus variants. They found that pemivibart is 25x less effective against KP.3.1.1 than the JN.1 variant. This is similar to data listed on Stanford's COVID Antiviral and Resistance database.
Special edition of Science magazine on Long COVID
This week, Science Translational Medicine had a special edition on Long COVID with the following articles:
Infection-associated chronic conditions: Why Long Covid is our best chance to untangle Osler’s web
Sex differences and immune correlates of Long Covid development, symptom persistence, and resolution
The cover image symbolizes the burden that individuals with Long Covid bear as a consequence of infection with SARS-CoV-2.
From: https://www.science.org/toc/stm/16/773
Here is information on a few of the articles from the Science Translational Medicine special issue:
Drs. Peluso, Hanson, and Deeks recommend that coordinated research is needed to be able to understand Long COVID and other infection-associated chronic conditions (IACCs) such as Myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME). Dr. William Osler taught doctors to listen to the patient, but in today’s more technological world, doctors rely heavily on diagnostic tests for diagnosis. No diagnostic tests exist for ME/CFS or Long COVID. The authors recommend studying sex differences in Long COVID and IACCs, antigen persistence, reactivation of latent viruses like EBV, and possible antiviral treatments. Understanding Long COVID will hopefully help us understand other IACCs as well.
Long COVID and other post acute infection syndromes affect females more than males with a difference in prevalence, symptoms, and potential causes. An article from Silva and Iwasaki focuses on “sex differences, gaps in current understanding, and the critical need for sex-based research” in Long COVID.
A group from University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill reviewed current and future animal models to be used for Long COVID pre-clinical research. Animal models discussed include different types of mice, ferrets, and non-human primates.
Drs. Antar and Cox from Johns Hopkins reviewed inflammatory biomarkers, preclinical models of Long COVID, clinical trial data and possible causes of Long COVID. Currently, there are no effective treatments for Long COVID. They recommend large studies in humans and animal models to find possible treatments for Long COVID.
From: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scitranslmed.ado2106
A group from Stanford shows sex differences in immune correlates after COVID infection. Males with Long COVID showed increased TGF-β signaling during acute infection, while females had reduced TGFB1 expression and elevated XIST, which is linked to autoimmunity. Long COVID patients exhibited reduced ETS1 across lymphocytes and had higher IL-4 in T cells, suggesting that ETS1 alterations may drive abnormal T helper 2 responses in Long COVID.
Other Long COVID articles from this week
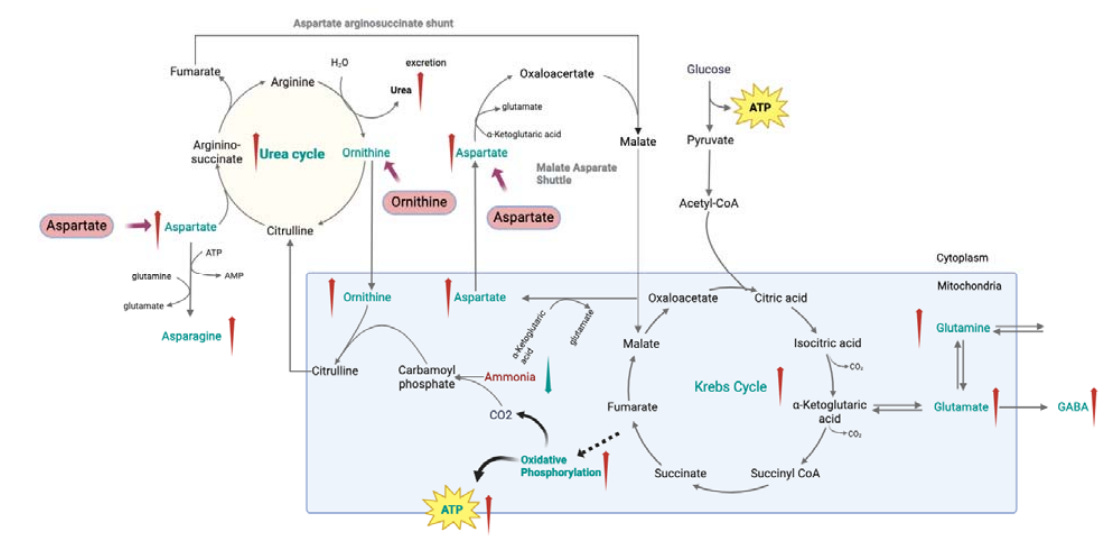
Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS) and Long COVID are complex conditions with overlapping metabolic symptoms. A study used genome-wide metabolic modeling to identify key metabolic abnormalities in muscle tissue from people with ME/CFS and found downregulated alanine/aspartate and arginine/proline pathways. Based on the findings from this study, the authors suggest that a combination supplement of L-Ornithine and L-Aspartate (LOLA) may alleviate symptoms in ME/CFS and Long COVID and should be tested in clinical trials.
Figure 4: L-Ornithine and L-Aspartate (LOLA) as a Potential Treatment Candidate for ME/CFS and Long COVID
From: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2024.06.17.599450v2.full.pdf
BC007 is a small molecule drug used to neutralize functional autoantibodies (fAABs). An initial case series of four Long COVID patients showed that BC007 was curative. However, a Phase 2, randomized, double-blind clinical trial of BC007 shows that BC007 does not work better than placebo to treat Long COVID.
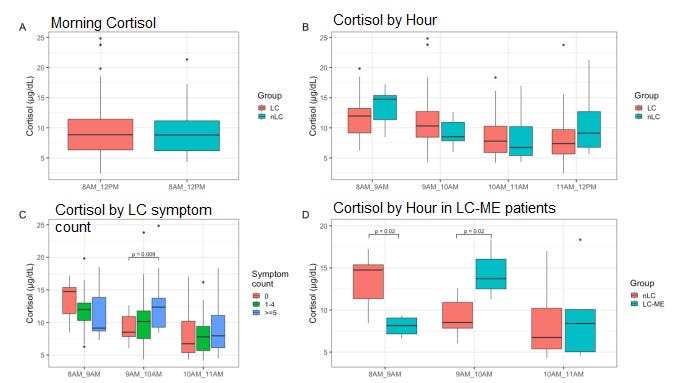
A new study from UCSF shows “no difference in overall morning cortisol concentrations between people with LC [Long COVID] (n=144) and those who fully recovered (n=56).” However, people with ME/CFS-type Long COVID were found to have low cortisol between 8 to 9am. People with severe Long COVID (>=5 symptoms) and those with ME/CFS-type Long COVID had high cortisol levels between 9 to 10am. The authors concluded that morning cortisol dynamics may be altered in some people with Long COVID.
From: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2024.11.07.24316777v1.full.pdf
Researchers evaluated EHR records from 295,000 patients in Massachusetts and made an AI phenotyping algorithm that could diagnose Long COVID with a diagnostic accuracy of 79.9% which is more accurate than using the Long COVID ICD-10 diagnosis code U09.9 to identify patients. The algorithm excluded symptoms that prior conditions could explain and included infection-associated chronic conditions. The algorithm estimated that the prevalence of Long COVID in their population was actually 22.8%.
Autoimmune blistering diseases (AIBD) like pemphigus and pemphigoid are rare diseases caused by autoantibodies that attack one’s own tissues causing painful blisters. A very large study of 112 million people shows that COVID infection significantly increases the risk of AIBD, but that vaccination against COVID can reduce the risk of these blistering diseases.
This concurs with another large study from last week’s newsletter that showed similar findings. In that study of almost 7 million people in South Korea from 2020 to 2022, researchers found significantly increased risks of autoimmune and autoinflammatory connective tissue disorders following COVID infection, especially in people with severe COVID-19 infection, those infected with the Delta variant, and in unvaccinated individuals. Autoimmune diseases included bullous pemphigoid (AHR, 1.62) in addition to ulcerative diseases like Behçet disease (AHR, 1.45), Crohn’s disease (AHR, 1.35), ulcerative colitis (AHR, 1.15), and other autoimmune diseases.
This week, there has been quite a lot of news on H5N1 avian flu. First, a Canadian teenager with no exposure to farm animals has been admitted to the hospital for a very severe case of H5N1, the source of which is unknown. Western Canada and western American states have seen an increase in poultry outbreaks of bird flu related to wild birds migrating south. The previously healthy teen has ARDS (acute respiratory distress syndrome) and is in the ICU.
Genetic analysis for the teen’s H5N1 virus shows that it contains mutations that may make it easier to spread from human-to-human. This is concerning. But, the case is being followed very closely and no other people have become sick with this variant of H5N1.
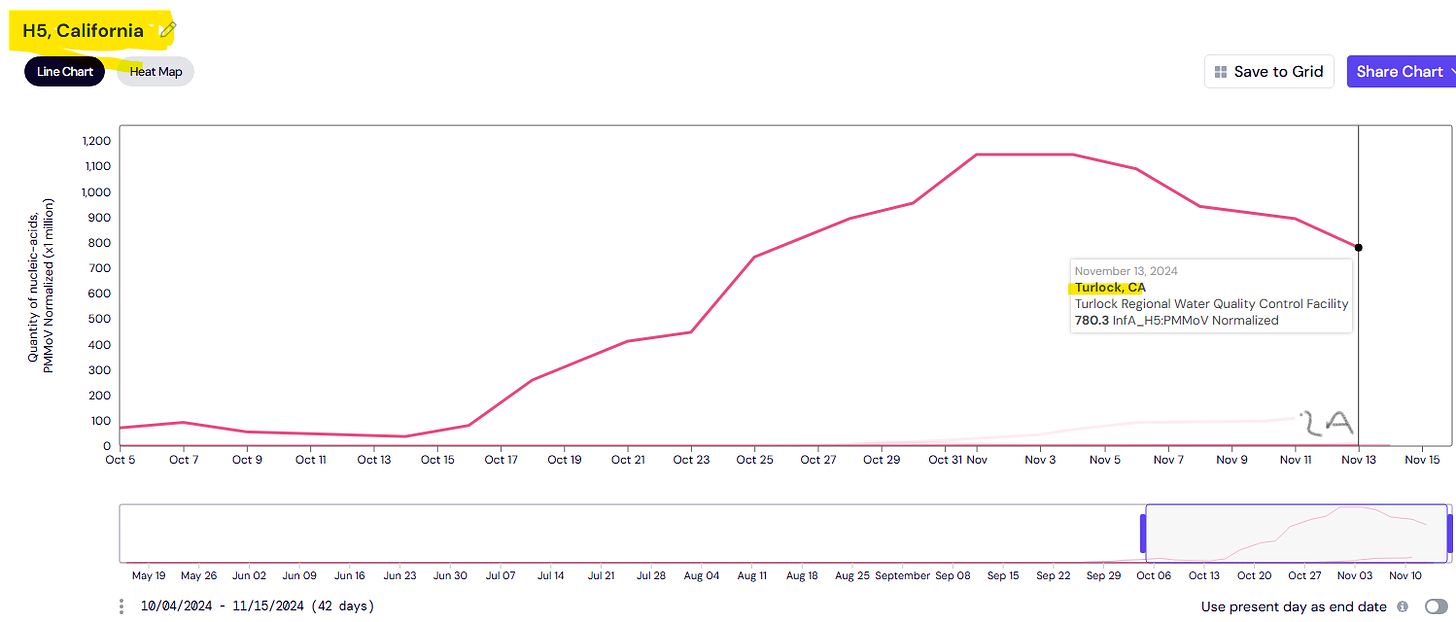
Here in California, some H5 bird flu virus has been found in wastewater from Lompoc, Los Angeles, Napa, San Francisco, Ontario, Paso Robles, Redwood City, Riverside, Sacramento, San Jose, Sunnyvale and Turlock. Turlock’s levels of H5N1 in wastewater are extraordinarily high, consistent with large dairy farms in the area.
From https://data.wastewaterscan.org/ looking up “Influenza A, H5 type, in California”
Yesterday, the Oregon Health Authority reported the state's first human H5 avian flu case which is linked to poultry. The California Department of Public Health (CDPH) reported 5 new H5N1 infections in farm workers, bringing the state total to 26. Per the CDC, a total of 52 people have been shown to be infected by H5N1 bird flu so far this year, although with a recent study showing 7% of dairy workers have antibodies to bird flu, many cases are going unrecognized.
A new study in AJOG shows that maternal RSV vaccination earlier in the recommended 32-36 week window (at least 5 weeks prior to delivery) results in the highest transplacental transfer of maternal RSV antibodies to the newborn.
Historically, American Indian and Alaska Native (AI/AN) children have had high rates of RSV-associated hospitalization and therefore, it was recommended that AI/AN children age 0 to 19 months in an Alaskan region receive a preventive monoclonal antibody called nirsevimab (Beyfortus). "For children in their first RSV season (292), nirsevimab effectiveness was
76% against medically attended RSV illness and 89% against RSV hospitalization. For children in their second RSV season (180), effectiveness against medically attended RSV illness was 88%." The authors concluded that Nirsevimab is effective for preventing severe RSV illness for infants in their first RSV season and young children in their second RSV season who are at increased risk for severe RSV, including all AI/AN children.
A new multimodal artificial intelligence model called EVO can interpret and generate new protein and genomic sequences on its own. Evo can predict the impact of mutations on how a protein will function. It has been released by Brian Hie’s lab to the public for other scientists to use. “This work is extremely significant,” says computational biologist Arvind Ramanathan of Argonne National Laboratory.
An AI algorithm combined with RNA editing-based blood biomarkers is able to differentiate between bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder with high accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity (82.5 %, 86.4 % and 80.8 %, respectively). Using this tool could help reduce diagnostic delays often seen with bipolar disease.
Trump appointed anti-vaxxer Robert Kennedy Jr. to be director of US Health and Human Services. The Senate will need to confirm this post. Funding structure and management may change at the NIH no matter who is finally selected. Already, RFK Jr recommends replacing 600 NIH employees on Jan 21, 2025.
People are stocking up on morning-after pills in case of changes to laws regarding contraception with the new administration. I highly recommend IUDs for long acting contraception that lasts for 3, 8 or 10 years and is easily removable when desired.
A new study shows that microplastics can help harmful bacteria and viruses such as Listeria monocytogenes, Escherichia coli, norovirus, and adenovirus to survive wastewater treatment. The microbes cling to microplastics and make a biofilm which makes it harder to break them down.
Sweet! A couple who were premature babies at the same time in the NICU were recently married. Their mothers kept in touch and reintroduced them to each other.
Have a good rest of your weekend,
Ruth Ann Crystal MD
















.jpg)
No comments:
Post a Comment