Here's the latest information-packed newsletter from Dr Ruth Ann Crystal:
------------------------------------------------
Acute respiratory illness levels are now LOW across America. Influenza B is decreasing and COVID cases are declining as well.
COVID
SARS-CoV-2 wastewater levels are at LOW levels according to the CDC in most places in the U.S., as are Emergency Department visits for COVID and COVID deaths.
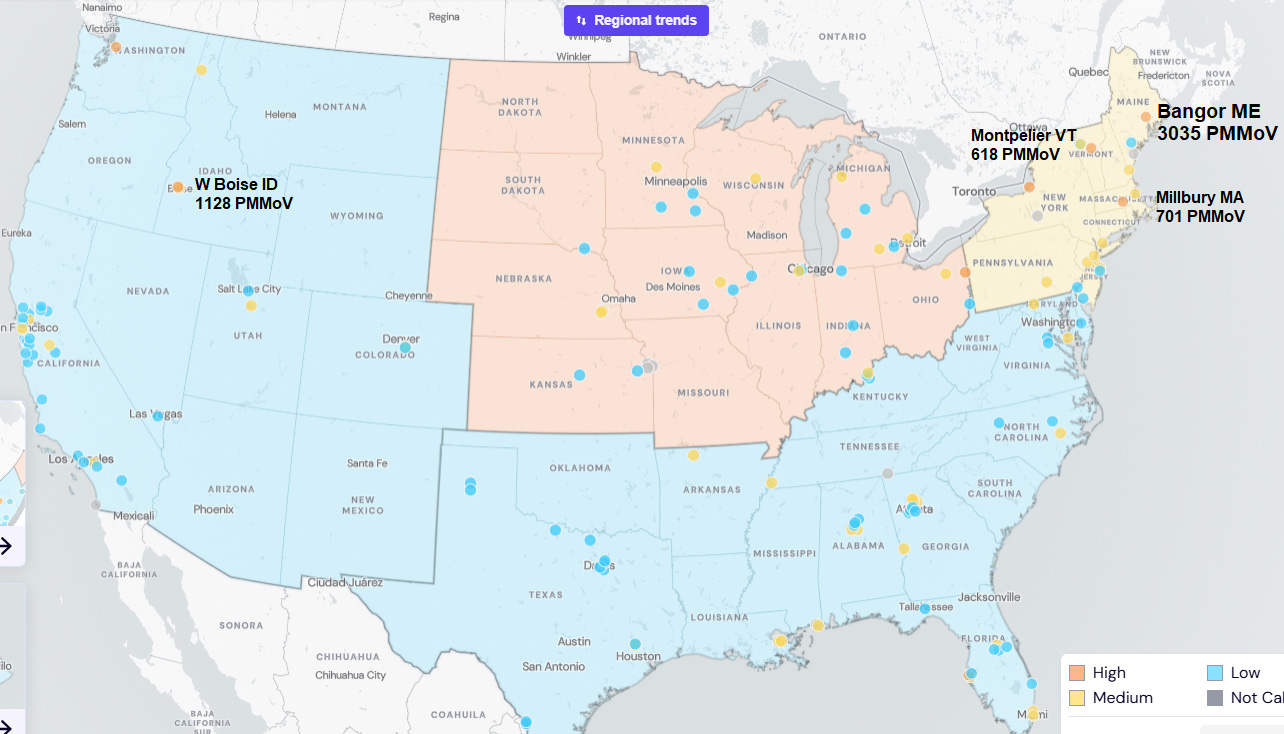
JP Weiland estimates about 220,000 new COVID infections per day in the United States with 1 in 152 Americans currently infected as of May 3. COVID transmission is slowly declining and is at low levels. Per WastewaterSCAN, the highest SARS-CoV-2 wastewater levels are in Bangor, Maine; Boise, Idaho; Millbury, MA; and Montpelier, Vermont. Most counties in California are reporting low wastewater levels, but San Luis Obispo County is very high this week.
LP.8.1 is still the dominant COVID variant without major challengers at this point. Our immunity is starting to wane and many people have not had a COVID booster since the fall, but transmission is low in most places right now.
From: https://data.wastewaterscan.org/
Antiviral treatments
Two new antiviral compounds, AVI4516 and AVI4773, developed by UCSF and the Gladstone Institute are broad-spectrum coronavirus MPro inhibitors that outperformed Paxlovid in preclinical models against SARS-CoV-2 and MERS. The new drugs show broad pan-coronavirus protection, a million-fold reduction in viral load compared to Paxlovid, exceptional brain penetration and minimal side effects. Researchers are pushing for clinical trials despite losing key federal funding, emphasizing their potential as shelf-stable treatments for future coronavirus outbreaks.
COVID and Mast Cells
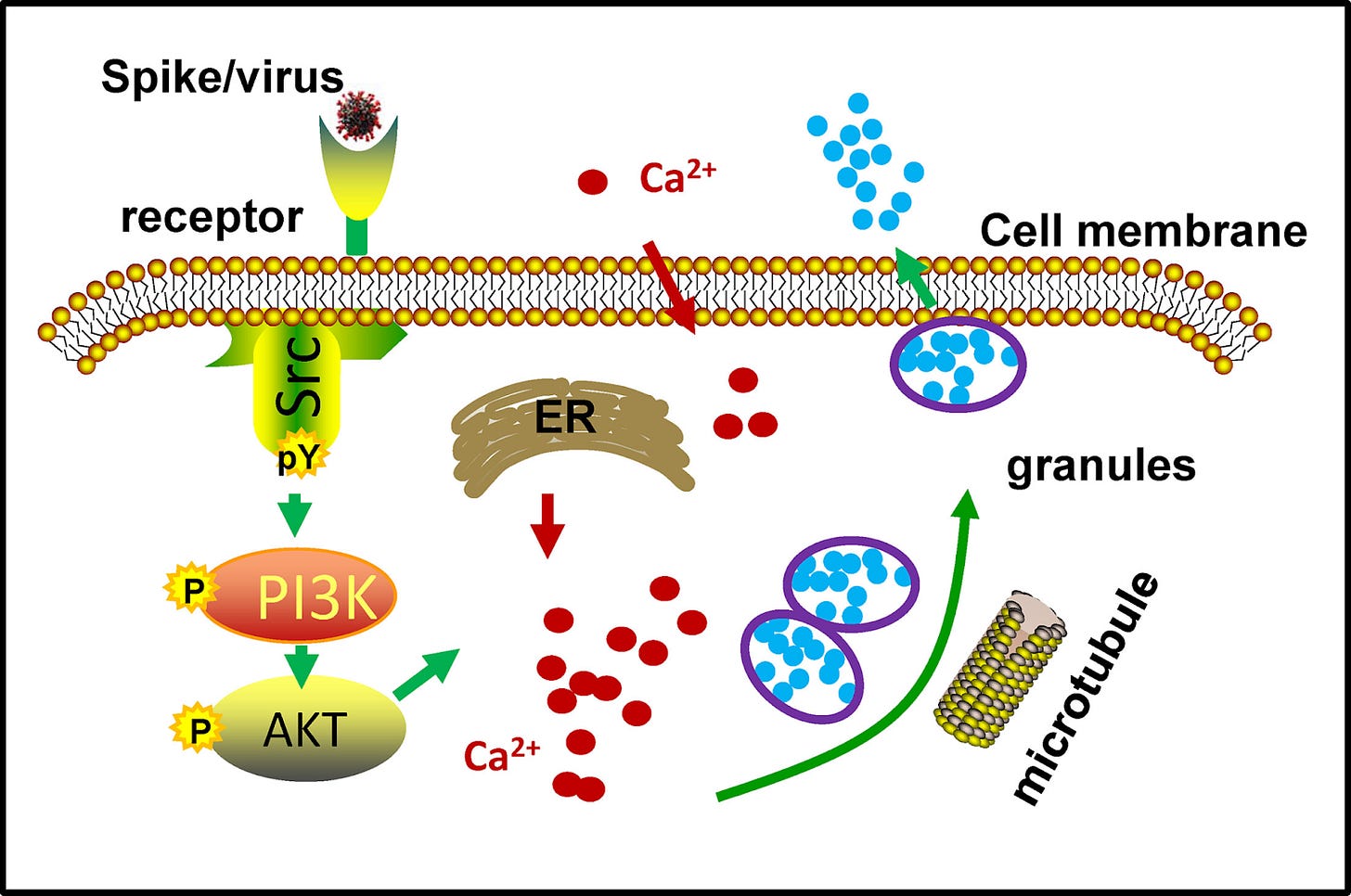
A new study from China shows that coronavirus spike proteins can trigger mast cell degranulation by binding to cellular receptors and activating the Src/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, leading to increased calcium levels and mast cell granule release. This mechanism was confirmed across several human coronaviruses and may contribute to the inflammation seen in COVID.
From: https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/jvi.00078-25
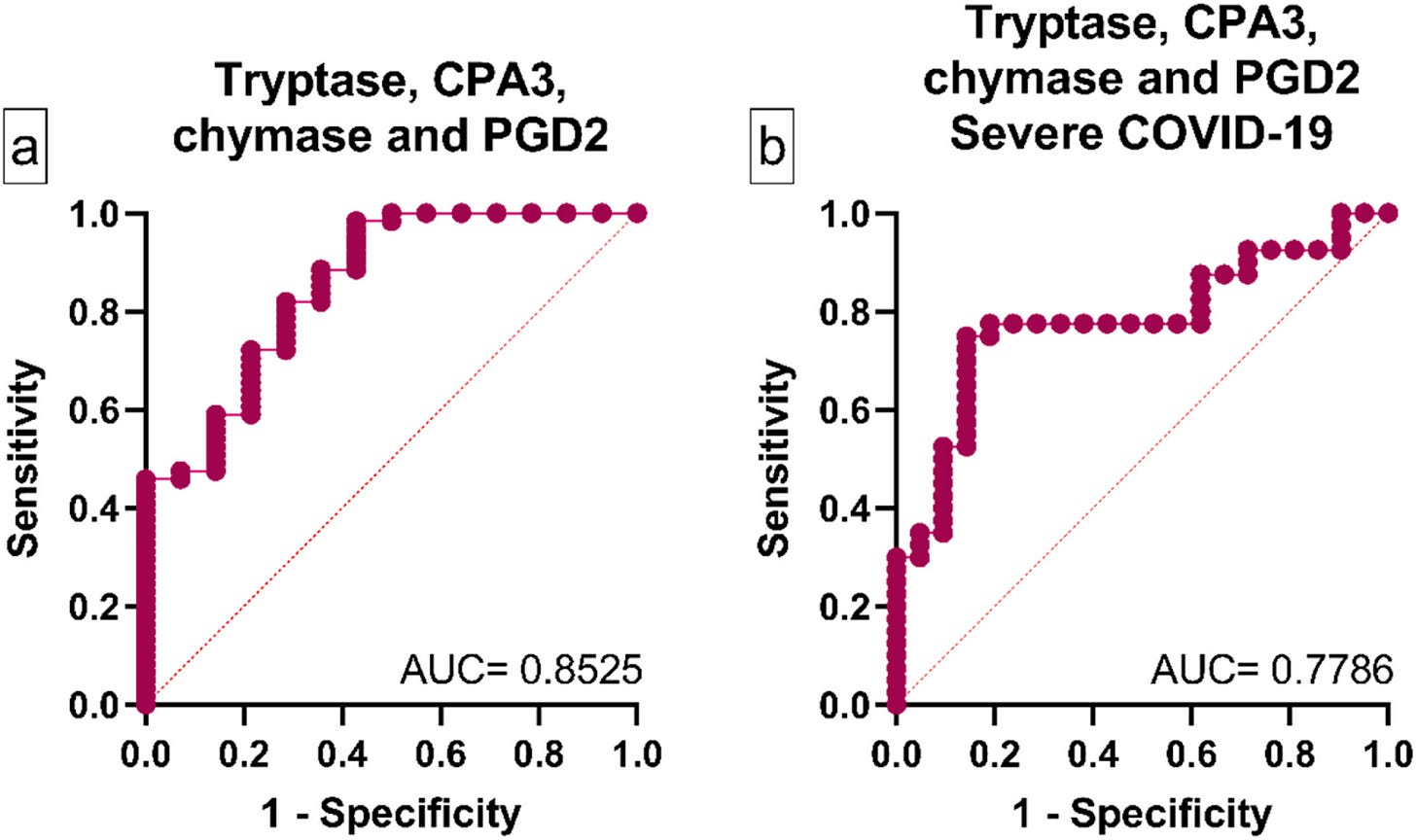
A group from Mexico found that serum levels of mast cell-derived mediators tryptase, CPA3, chymase, and prostaglandin D2 were elevated in COVID patients and correlated with markers of inflammation and coagulopathy. While individual markers showed limited ability to predict severe disease on their own, a combined profile improved predictive power, suggesting that a mast cell activation signature may serve as a useful biomarker and therapeutic target in COVID and other inflammatory conditions.
From: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0165247825000598
About 20% of the US population have chemical intolerance and react to low levels of chemicals that are used in everyday life. Increased use of disinfectants and sanitizers during the pandemic worsened symptoms for many, leading to health challenges and social isolation. A new study from San Antonio, Texas showed that people with chemical intolerance were found to have a higher prevalence of COVID infections associated with more severe symptoms and also had a higher risk of Long COVID. In theory, Mast Cell Activation Syndrome (MCAS) and chemical intolerance could possibly be related.
Long COVID
Stanford researchers studied 24 patients with Long-COVID-associated POTS (LC-POTS) to identify underlying causes of autonomic dysfunction. Compared to healthy COVID-recovered controls, LC-POTS participants showed greater increases in heart rate during tilt-table testing, higher norepinephrine levels, impaired sweat responses, and reduced small nerve fiber density. Surprisingly, 8.7% had phosphorylated alpha-synuclein (P-Syn) deposits in skin biopsies which is a protein associated with Parkinson’s Disease. The study supports the idea that autonomic dysfunction in LC-POTS is driven by multiple pathophysiological mechanisms “including orthostatic tachycardia, sympathetic adrenergic hyperactivity, small fiber neuropathy, and dermal P-Syn deposition.”
A new study in Nature used high-resolution immune profiling and proteomics to compare people with Long COVID to healthy COVID convalescents. Although immune cell types and T cell responses were mostly similar between groups, individuals with Long COVID had weaker neutralizing antibody responses and elevated levels of co-inhibitory receptors (like PD-1 and TIM-3) on non-spike-specific CD8+ T cells. Plasma protein analyses linked breathlessness in Long COVID to a distinct protein signature associated with inflammation and cell death, particularly involving CD40, IL-18, and NF-κB pathways. Persistent respiratory symptoms after COVID may reflect localized lung inflammation and damage from residual antigen exposure rather than broad immune dysfunction.
H5N1
Top virologists from more than 40 countries are urging global leaders to take immediate action against the growing threat of H5N1 avian flu. They emphasize strengthening global surveillance, investing in preparedness, and improving response capabilities to avoid a future pandemic. Without action, the experts warn that the virus could evolve to spread more easily among humans.
The CDC canceled a planned National Academy of Sciences workshop focused on preventing human H5N1 bird flu infections, despite growing concerns over the virus's spread among U.S. cattle and poultry. The event was set to train farmworkers and veterinarians on proper use of personal protective equipment (PPE), but was abruptly terminated by the Department of Health and Human Services.
Measles
As of May 1, 2025 in the US, a total of 935 Measles cases were reported by 29 states, 13% have been hospitalized for measles complications and 3 deaths have been reported.
Ontario, Canada has a major Measles outbreak with more than 1,200 cases reported this year. MMR vaccination rates are low in Ontario with only 38% of 5 year olds and 70% of 7 year olds vaccinated.
"Less than 80% of eligible children in Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, North Macedonia and Romania were vaccinated with MCV1 in 2023”. Low vaccination rates due to pandemic disruptions fueled resurgence of measles in 2024 particularly in some WHO European Region countries like Romania (30,692 cases) and Kazakhstan (28,147 cases).
Vaccines, HHS, and Misinformation
Health and Human Services (HHS) Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr. continues to spread misinformation about vaccines. In recent interviews, he falsely claimed that the MMR vaccine contains "aborted fetus debris" and advised parents to "do your own research" rather than trust decades of proven vaccine science. The MMR vaccine does not contain fetal tissue, and it has safely protected against Measles, Mumps, and Rubella for over 50 years.
Instead of promoting vaccination amid rising measles cases, RFK Jr. has now called for the development of new measles treatments. We do not need to waste time and money on new measles treatments when the MMR is proven to protect 97% against Measles. As Benjamin Franklin famously advised, "An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure."
Kennedy is also now planning placebo vaccine trials for all vaccines, which experts say violate medical ethics since the effectiveness of existing vaccines is well established and giving a placebo would be akin to malpractice. Separately, FDA commissioner Marty Makary is reviewing whether to authorize updated COVID boosters for next winter citing “a lack of data on booster shots” despite the fact that billions of doses of COVID vaccines have been given safely worldwide. As of May 2023, 677 million doses of COVID vaccines had been given in the United States alone.
Pertussis (Whooping Cough)
Whooping cough (Pertussis) infections in the U.S. have more than doubled this year, with 8,077 cases reported through mid-April—marking the worst outbreak in 70 years. At least four deaths, including two infants, have been linked to the surge which experts attribute to waning immunity and falling childhood vaccination rates. With fewer than 93% of kindergartners fully vaccinated against pertussis for the 2023–2024 school year, health officials warn that protection against vaccine-preventable diseases like measles and pertussis is weakening. The CDC urges up-to-date vaccinations and boosters especially for infants, pregnant individuals, and adults who have not been immunized.
Other news
A Stanford study shows that women who experienced hypertensive disorders like preeclampsia during pregnancy show changes in their blood protein profiles, especially in complement and coagulation pathways, for years. Proteomic signatures identified during the postpartum period continued to distinguish between affected women and controls in mid-life, suggesting a biological link between pregnancy complications and later cardiovascular disease risk.
A preliminary trial and studies in mice suggest a link between fibromyalgia chronic pain and alterations in the gut microbiome. Supplementing with specific gut microbes appeared to alleviate chronic pain symptoms in some patients.
A high-fat, low-fiber Western diet prevented gut microbiome recovery in mice after antibiotics, while a fiber-rich chow diet enabled full recovery of microbial diversity and function. The Western diet suppressed microbial diversity, reduced functional gene recovery, and prevented the re-establishment of metabolically supportive cross-feeding between microbes. The study showed that diet was more important than fecal transplants for restoring gut health, highlighting the need for complex carbohydrates to support recovery after antibiotics.
Researchers found that imbalances in the nasal microbiome may be linked to both smell loss and cognitive decline in older adults. These changes may affect the brain through inflammation or other pathways, suggesting a possible early warning sign of neurodegenerative diseases. The findings could help identify new targets for early intervention in cognitive decline.
New government data shows that a single dose of the HPV vaccine provides strong protection against cancer-causing infections, similar to the traditional two-dose regimen. Giving only one dose could really help simplify vaccination efforts.
A case-control study found molecular similarities between Human Papillomavirus (HPV) viral proteins, particularly HPV18, and key receptors involved in thyroid eye disease (TED), suggesting that viral mimicry may trigger autoimmune responses. Patients with TED had significantly different levels of HPV18 antibodies in orbital tissue compared to controls, with the strongest differences seen in those with active TED.
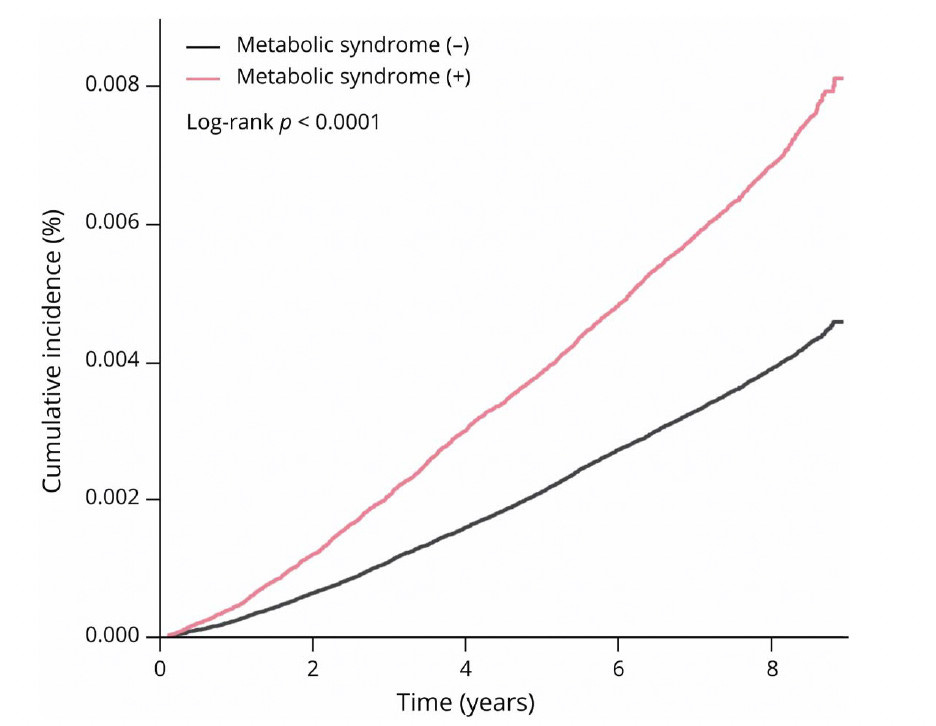
A large study from South Korea found that metabolic syndrome increases the risk of developing dementia before age 65 by 24%. The risk was even higher among women and those diagnosed with the condition in their 40s. Researchers recommend early lifestyle changes to lower the risk of young-onset dementia.
From: https://www.neurology.org/doi/abs/10.1212/WNL.0000000000213599
In April, the Guinness World Records smallest dog Pearl met up with the world’s tallest dog Reggie. Despite Pearl the Chihuahua being 3.6 inches tall and Great Dane Reggie 3 foot, 4 inches tall, the unlikely duo played happily together.
From: Natalie Behring/Guinness World Records
Have a great week,
Ruth Ann Crystal MD















.jpg)
No comments:
Post a Comment