-----------------------------------------
This week’s newsletter includes updates on winter respiratory viruses including COVID, Influenza (flu), RSV, Whooping Cough, H5N1 Bird Flu and more. Unfortunately, there is a lot of government news related to decreasing vaccine access that I have included as well.
Nationally, Influenza activity is increasing with largest increases seen among children and young adults and in the northeastern and mountain west areas. Similar to what is being seen in other countries, the United States are expecting a bad flu season this year, at least partially due to the new subclade K variant of Influenza A. It is important to stay home if sick, wear a mask indoors especially if in crowds and to wash your hands often in order to avoid getting the flu. The CDC recommends that everyone 6 months and older who has not yet been vaccinated this season get an annual influenza (flu) vaccine.
From: https://www.cdc.gov/fluview/surveillance/2025-week-48.html
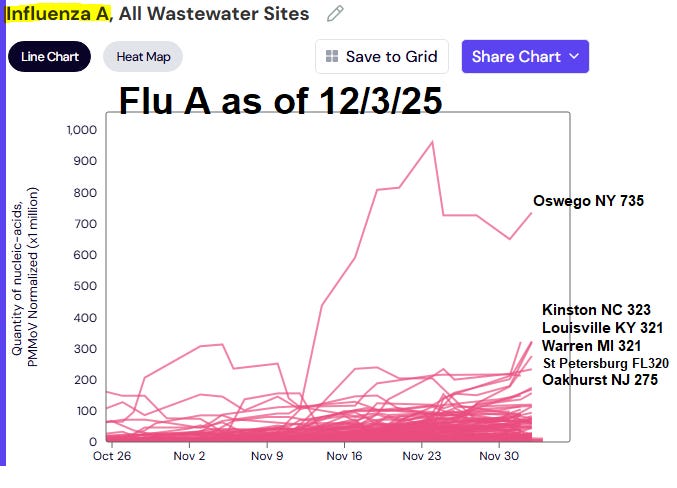
Outpatient clinic visits for Influenza-like illness (ILI) were HIGH in New York state, including New York City, Louisiana, Colorado, and Puerto Rico through 11/29/25. According to the CDC, Flu was especially HIGH in wastewater in Kentucky and Louisiana as of 11/29/25. As of Dec 3rd, WastewaterSCAN shows high levels of Influenza in wastewater in Oswego NY, Kinston NC, Louisville KY, Warren MI, St Petersburg FL, and Oakhurst NJ.
From: https://data.wastewaterscan.org/
According to the CDC, RSV activity in Southern and mid-Atlantic states is increasing. RSV is very high in Louisiana. The RSV vaccine is recommended in pregnancy to help protect the baby and is also recommended for adults ages 50 to 74 with risk factors and all adults over age 75. Babies can get RSV antibodies to protect them from October through March.
Per the CDC, COVID levels were VERY HIGH in Arizona, HIGH in Indiana and Vermont, and MODERATE in Nebraska and Alabama through 11/29/25.
WastewaterSCAN omits 12 states including Arizona, but is more current than CDC data. It shows MODERATE levels of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater across the US, with HIGH levels of COVID seen in the Northeast and Midwest.
From: https://data.wastewaterscan.org/
JP Weiland did not have an update about COVID this week. Michael Hoerger and the PMC19 data will update their data on Monday. Through 11/22/25, they calculated that about 1 in 103 people was infected with COVID in America. Using CDC data from 12/1/25, Hoerger predicts that 1 in 29 people in Tennessee had COVID and that 1 in 42 in Vermont were infectious. You can look up risks for COVID for your state using PMC19’s estimates here.
According to Bob Hawkins, COVID levels are low across the United Kingdom, but Flu and RSV activity is increasing significantly. The UKHSA dashboard shows that the Influenza positivity rate is a whopping 36% for children ages 5 to 14 years.
The CDC has not updated the COVID variant page since 8/28/25, but variant XFG continues to be dominant in the US and in other countries globally.
COVID variant BA.3.2, now nicknamed “Cicada” according to Raj Rajnarayanan, is starting to slowly spread in Germany. Ryan Hisner believes that BA.3.2 will eventually overtake the JN.1 descendants (including XFG) because it is already able to compete somewhat against the current dominant variant.
In a University of Minnesota a target trial emulation study of 248 adults, early Metformin use by day 6 of acute COVID infection was associated with a 53% lower risk of Long COVID compared to fluvoxamine, fluticasone, ivermectin, or montelukast.
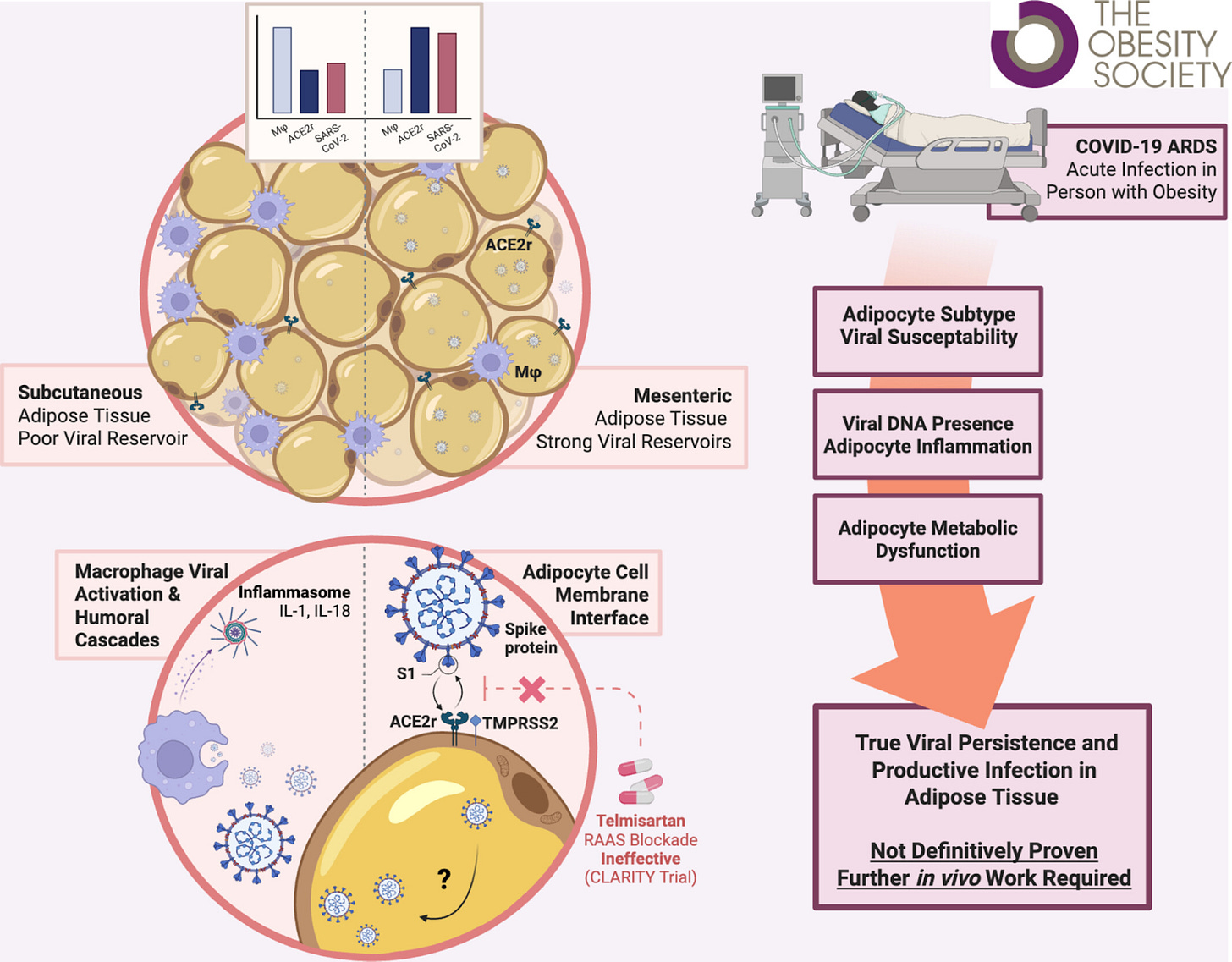
Researchers at Cork University reviewed human, animal, and in-vitro studies evaluating SARS-CoV-2 infection in adipose tissue, highlighting evidence that the virus can enter adipocytes (fat cells), may replicate within fat, which could then act as a viral reservoir contributing to prolonged inflammation or delayed SARS-CoV-2 clearance. These mechanisms may help explain why individuals with obesity experience more severe acute COVID infections and higher risk of persistent symptoms.
From: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/oby.70093
“SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination are associated with a broad range of skin manifestations, including chilblains, urticaria, morbilliform and papulovesicular rashes, purpuric-necrotic lesions, and autoimmune flares. The dermatologic patterns reflect differences in the timing and nature of type I interferon (IFN-I) responses.” Rapid IFN-I production can restrict viral replication, but can cause local inflammation (such as chilblains or COVID toes), whereas a delayed response may lead to broader viral spread and systemic skin reactions.
Figure 2. Cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19. (a) urticarial rash, (b) morbilliform eruption, (c) papulovesicular rash, (d) livedoid and purpuric-necrotic lesions, and (e) chilblains.
From: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0952791525001323?via%3Dihub
Researchers at Skåne University Hospital in Sweden assessed 396 children and documented a 30% increase in the incidence of Type 1 Diabetes during the COVID-19 pandemic. Notably, children who had SARS-CoV-2 antibodies at the time of their diabetes diagnosis were at least three times more likely to also exhibit signs of thyroid autoimmunity, indicating a potential viral trigger of SARS-CoV-2 for multiple autoimmune diseases.
Tattoo ink often persists in lymph nodes for life. Using a mouse model, researchers from Switzerland investigated how tattoo ink influences immunity. They found that tattoo pigments accumulated in the draining lymph nodes, produced persistent inflammation, and altered immune responses to vaccination with a reduced response to the mRNA COVID vaccine and an enhanced response to a UV-inactivated influenza vaccine.
A study of 1,474 app users found that being vaccinated during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle led to 35% more side effects, such as fever and fatigue, but also led to more durable protection against COVID infection. Menstrual cycle timing may modestly shape immune responses.
A global review of over 9,000 studies showed that vaccination lowers Long COVID risk by at least 23%, with boosters offering even better protection. The findings reinforce vaccination as one of the strongest population-level tools to reduce post-acute COVID morbidity.
Experts from Yale reviewed historical epidemics that were associated with post-acute infection syndromes (PAIS) like Long COVID. Such illnesses have been documented for centuries. Seeing Long COVID as part of a broader pattern may help guide research and care for today’s long haulers and prepare for future epidemics or pandemics.
Figure 1 Epidemics and their post-acute sequelae throughout modern history.
From: http://cell.com/trends/immunology/fulltext/S1471-4906(25)00267-4
Researchers in Germany used non-invasive retinal imaging (OCTA) to examine people with Long COVID who initially had mild infections. They found enlargement of the Foveal Avascular Zone (FAZ) in Long COVID, which signals microvascular injury. The FAZ was especially enlarged in participants with Long COVID fatigue, and the degree of increase closely tracked with fatigue severity. Similar FAZ enlargement is seen in conditions such as diabetes and glaucoma, which can predict future vision problems. These results suggest OCTA retinal imaging could be used as a non-invasive tool to monitor microvascular changes in Long COVID.
This week, there were 2 different articles on extracellular vesicles and Long COVID. Researchers in Italy analyzed extracellular vesicles (EVs) from 32 participants (16 Long COVID patients vs.16 controls) and found that EVs from Long COVID patients carried dysregulated miR-204, which activated the p53 stress pathway and increased RUNX2 expression in recipient cells. These EVs triggered mitochondrial dysfunction, impaired cellular metabolism, and heightened oxidative stress compared with EVs from healthy controls. The findings suggest that circulating EVs act as molecular drivers of persistent inflammation and tissue dysfunction in Long COVID.
A UCSF and Aethlon Medical study of 45 people found that Long COVID patients have higher mannosylated extracellular vesicles (EVs), which can be removed using a Galanthus nivalis agglutinin (GNA) resin in a Hemopurifier. The preprint study points to a possible biomarker (mannosylated EVs) and a new treatment target for Long COVID.
Researchers in Manaus, Brazil followed 80 COVID survivors for two years to examine persistent gastrointestinal symptoms. They found that 38% continued to experience issues such as reflux, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort, and that individuals with ongoing symptoms showed delayed elevations in IL-6, suggesting long lasting inflammation. The findings highlight the persistence and biological underpinnings of post-COVID gastrointestinal disease.
At the University of Iowa, researchers evaluated 12 Long COVID patients approximately 32 months after infection to explore links between lung physiology and brain function. They found that impaired alveolar gas exchange of oxygen in the lungs was associated with worse sleep quality, increased cerebral blood flow, and subtle deficits in executive function, even when standard cognitive tests appeared normal. The findings suggest that chronic lung abnormalities may contribute to the cognitive complaints frequently seen in Long COVID.
PolyBio Research Foundation president Amy Proal posted this week with a “message to the longevity community: To actually extend human healthspan we must curb the activity of the pathogen hackers that persist in our bodies.” She pointed to her TedX talk and I also found this article from PolyBio on how infections can be major drivers of aging.
There were 3 articles this week on causes of Long COVID pain. King’s College London researchers provided direct evidence of the mechanism behind Long COVID pain using a mouse model and antibodies from humans. When transferred into mice, autoantibodies from Long COVID patients with pain and fatigue immediately induced pain-like behavior and measurable nerve damage in mice, confirming that these self-attacking antibodies are the direct cause of chronic pain and sensory dysfunction.
Belgian researchers also showed that IgGs from Long COVID patients bind to sensory neurons and cause pain symptoms in mice without affecting cognition. This work strengthens evidence for autoimmune drivers of Long COVID sensory and pain syndromes.
Brazilian researchers showed in a preprint that SARS-CoV-2 spike protein fragments (peptides) can activate TLR4 pathways and microglia in the spinal cord in mice, triggering pain. It offers another biological explanation for the persistent pain reported in Long COVID.
As of December 2, 2025, a total of 1,828 confirmed measles cases were reported in the United States, with 12% of cases hospitalized (214 of 1828) and 3 confirmed deaths from measles. Two doses of the MMR vaccine are 97% effective in preventing measles.
Dr. Ralph Abraham, a known vaccine skeptic, was appointed as the CDC’s second-highest ranking leader last week. This appointment, given his history of calling COVID vaccines “dangerous,” signals a controversial shift in the direction of the United State’s primary public health institution. Dr. Jeremy Faust highlighted that Dr. Ralph Abraham is not board-certified, is openly anti-vaccine, and has been one of the nation’s highest prescribers of ivermectin and opioids.
Nearly 90% of the FDA’s senior leaders from a year ago have departed, a wave of turnover that began after Dr. Peter Marks resigned when he refused to grant VAERS editing access to Robert F. Kennedy Jr.’s team. Marks’ exit, followed by Richard Pazdur’s sudden retirement this week, highlights a year of rapid, dramatic upheaval that leaves only three senior FDA officials still in place. Pazdur, who had replaced George Tidmark, has now been replaced by Tracy Beth Hoeg. “The appointment of Hoeg, a COVID vaccine skeptic and close aide to FDA Commissioner Marty Makary, comes as U.S. Health Secretary Robert Kennedy Jr. makes stark changes at the agency.” Not surprisingly, the ACIP committee then disastrously changed policy this week on Hepatitis B vaccination for newborns (see below).
From: https://www.biospace.com/fda/pazdurs-sudden-exit-leaves-just-three-veterans-in-fdas-senior-ranks
This week, FDA official Vinay Prasad proposed sweeping new vaccine-testing requirements, including randomized trials in pregnant people, claiming without evidence that COVID vaccines caused 10 child deaths. Experts emphasized that this is not true and that vaccines have prevented millions of deaths globally. Public health leaders warn that adopting these standards could severely restrict access to routine immunizations and undermine long standing evidence showing vaccines are safe and essential during pregnancy.
Hepatitis B infection can cause liver damage and can lead to liver cancer. 1 in 4 children with chronic Hepatitis B will die from complications of the disease. For decades, the CDC has recommended that all babies be vaccinated against Hepatitis B at birth. Friday, “after contentious discussion, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) voted 8-3 to drop the recommendation for a universal birth Hepatitis B vaccine dose” and suggested that babies get a blood test to check antibody levels before doses 2 and 3 of the vaccine series. The universal birth Hepatitis B vaccine dose has prevented over 500,000 childhood infections and an estimated 90,100 childhood deaths since 1991. Public health experts warn that delaying the first vaccine dose, which is intended to protect US children from maternal transmission, could lead to thousands of preventable childhood infections annually.
Los Angeles County Public Health warned in a tweet: “For more than three decades, universal hepatitis B birth dose vaccination has been a cornerstone of perinatal hepatitis B prevention in the United States. The decision to end universal birth dose recommendation is not based on new evidence suggesting that hepatitis B vaccine birth dose is unsafe or ineffective. All existing data suggest that the universal birth dose of hepatitis B vaccine is consistently safe and results in life-long protection after the vaccine series is completed.” LA County will continue following existing California Department of Public Health hepatitis B vaccination guidelines recommending that all children receive hepatitis B vaccine at birth.
From: Los Angeles County Public Health
A third baby has died this year from Whooping Cough (Pertussis) in Kentucky as vaccination rates fall. The tragedy highlights how easily Pertussis can claim the lives of babies who depend on herd immunity from their parents and the community. Public health leaders are urging maternal Tdap vaccination and timely infant immunization to prevent more infant deaths.
ProPublica reports that U.S. agencies, including USDA, have downplayed scientific evidence showing that H5N1 bird flu can be transmitted through the air between mammals, citing concerns raised by multiple research groups. Scientists warn that ignoring airborne transmission risks could leave the United States unprepared for a potential spillover event, especially as H5N1 continues to evolve in dairy cattle and other species. The investigation highlights gaps in surveillance, transparency, and biosecurity policy that could hinder early detection of a pandemic threat.
UCSF ran a successful proof-of-concept study of triple immunotherapy in ten people with HIV on antiretroviral therapy (ART). They combined the following three approaches: 1) HIV therapeutic vaccination, 2) passive transfer of broadly neutralizing antibodies (bNAbs) and (3) a toll-like receptor 9 agonist (lefitolimod) during ART suppression, followed by repeat bNAb administration at the time of ART interruption. HIV infection was controlled without ART in seven of the ten participants of this study.
Epstein-Barr virus has been implicated in Multiple Sclerosis, Lupus and some cancers. A new NIH study of 23 people found that Brincidofovir blocked EBV reactivation in vitro in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from healthy donors and from Multiple Sclerosis patients pointing to a possible new antiviral approach for EBV-linked disease.
A legal filing released with newly unredacted information shows that Meta (Facebook’s parent company) deliberately halted internal research that showed that social media use caused harm to its users. The research purportedly found that individuals who stopped using the Facebook platform subsequently reported becoming less depressed and anxious, raising concerns about the company’s commitment to user mental health and transparency.
Researchers at Leiden University in the Netherlands reviewed evidence on how adolescents can build resilience to digital misinformation. They highlight that critical-thinking training, media literacy education, and supportive social environments improve young people’s ability to detect false content and resist manipulation. The authors emphasize that early, structured interventions help protect adolescent well-being in a digital landscape increasingly shaped by misinformation.
Having a dog as a teenager may improve mental well being and sociability, at least partially through the microbiome. Researchers in Japan studied adolescents and found that those who owned dogs had distinct oral microbiota profiles and better mental health compared with peers without pets. In follow-up mouse experiments, transferring dog-associated oral microbiota improved social behavior in mice, suggesting a causal role for microbial shifts. Specific Streptococcus ASVs correlated with well-being in both human adolescents and in mice, indicating a shared microbiome–behavior link.
A drunk raccoon was found passed out on a Virginia liquor store floor after it broke in and sampled the spirits. His drink of choice? Scotch. The raccoon was checked out by animal control and was released back into the wild once he sobered up.
From: https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/cy8jnxxm70jo
I will be taking off some time over the holidays, but plan to be back to my usual weekly news in January.
Happy Holidays!
Ruth Ann Crystal MD






















.jpg)
No comments:
Post a Comment