Respiratory Diseases
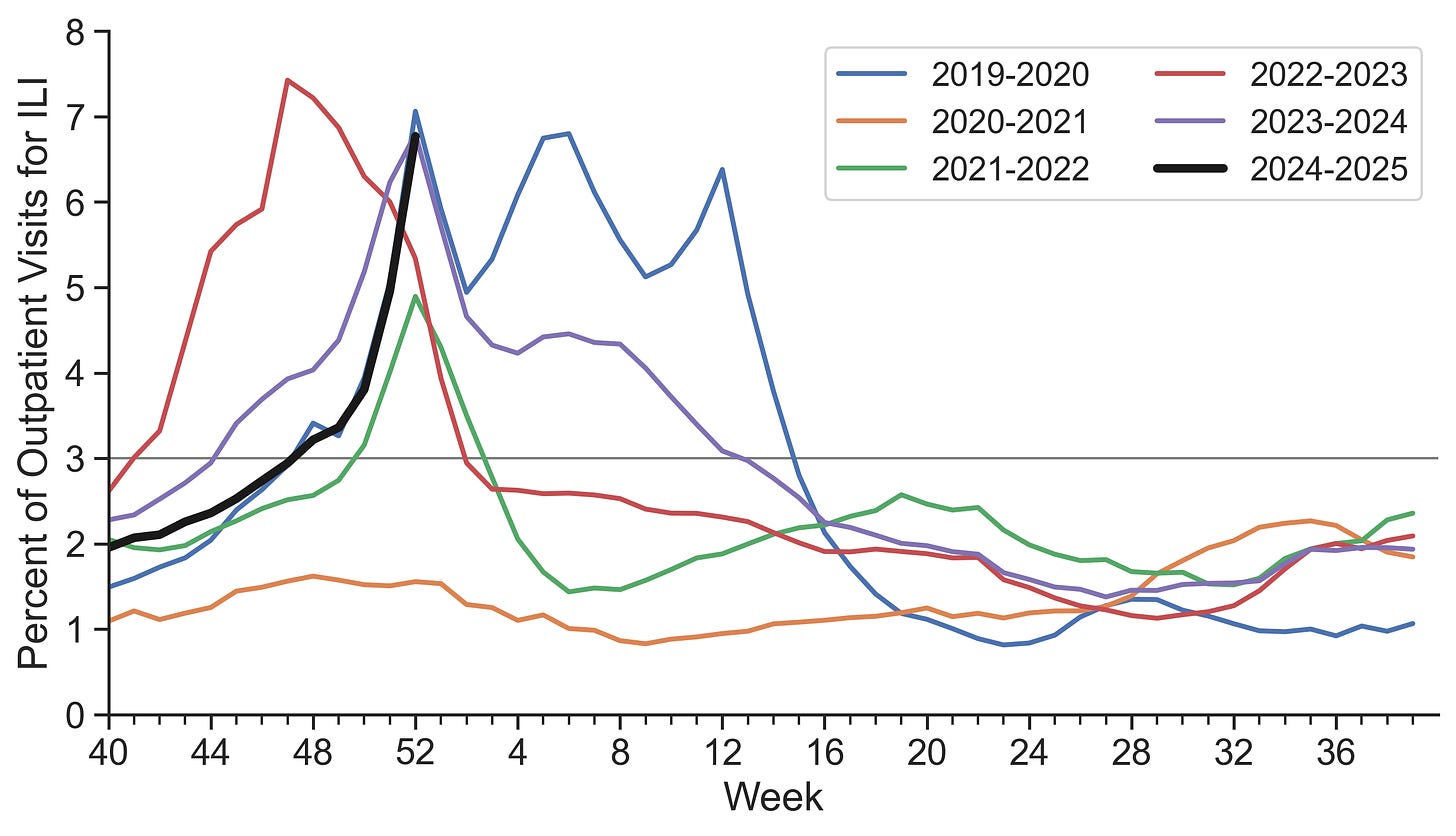
We’re likely at or near peak season, and there is a lot going around out there. Outpatient visits high 8.6%, a big jump from 5.0 % the week prior.
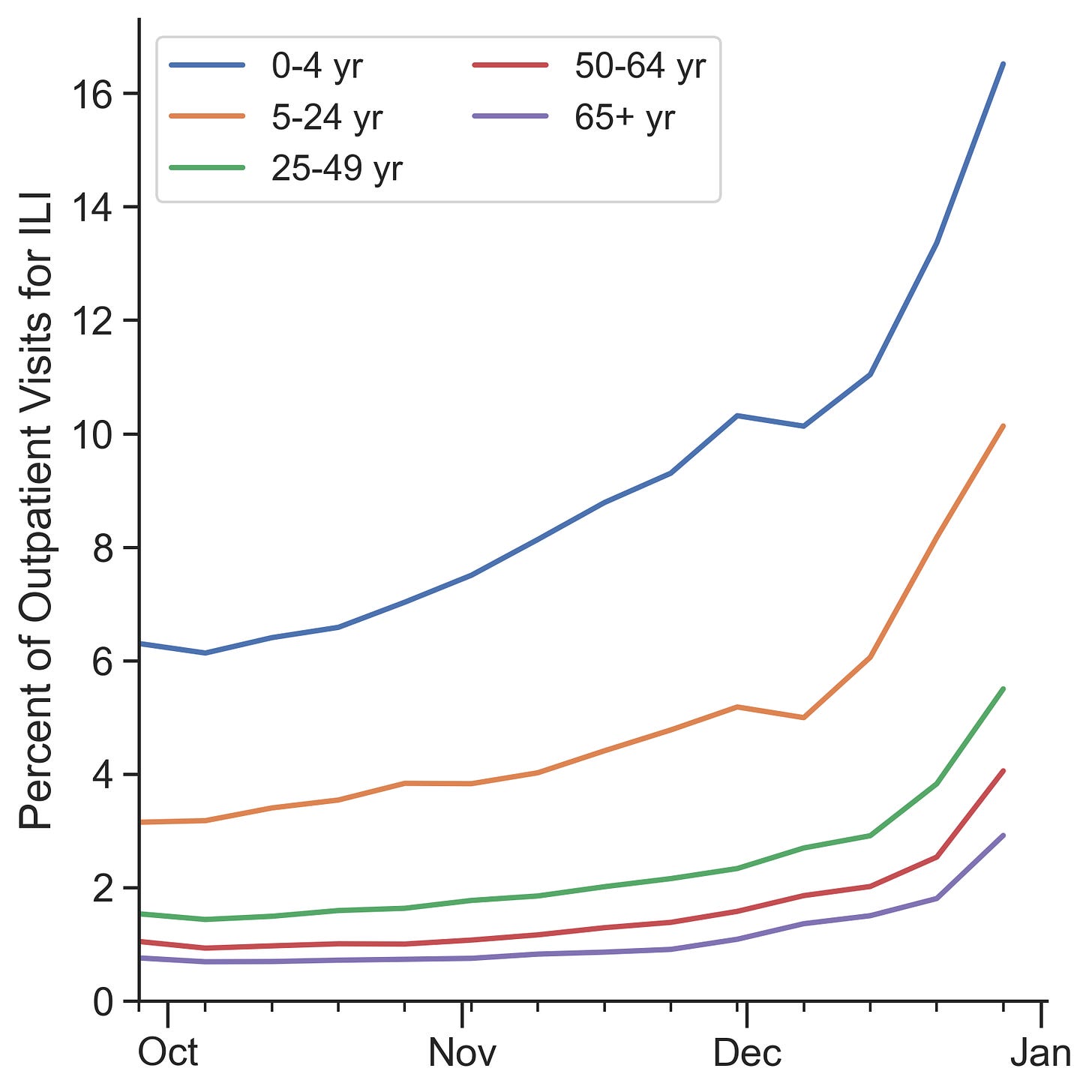
As always, kids are worst off. Children aged 0-4 years are experiencing the highest rates at 16.5% of visits, followed by school-age children and young adults (5-24 years) at 10.1%. Adults range from 5.5% in those 25-49 years to 4.1% in those 50-64 years, and 2.9% in those 65 and older. All age groups saw a jump from the previous week, with older adults showing some of the steepest relative increases.
ILI activity is most intense in the South and West, with multiple states in these regions reporting outpatient visit percentages above 7%. The South is experiencing widespread high activity, led by states reporting between 6-9% of visits for ILI. The Western region shows particularly intense activity in Mountain states, with several reporting sharp increases to levels above 8%. The Midwest is accelerating too, with visit percentages generally ranging from 3-6%. The Northeast has the lowest regional activity.
COVID-19
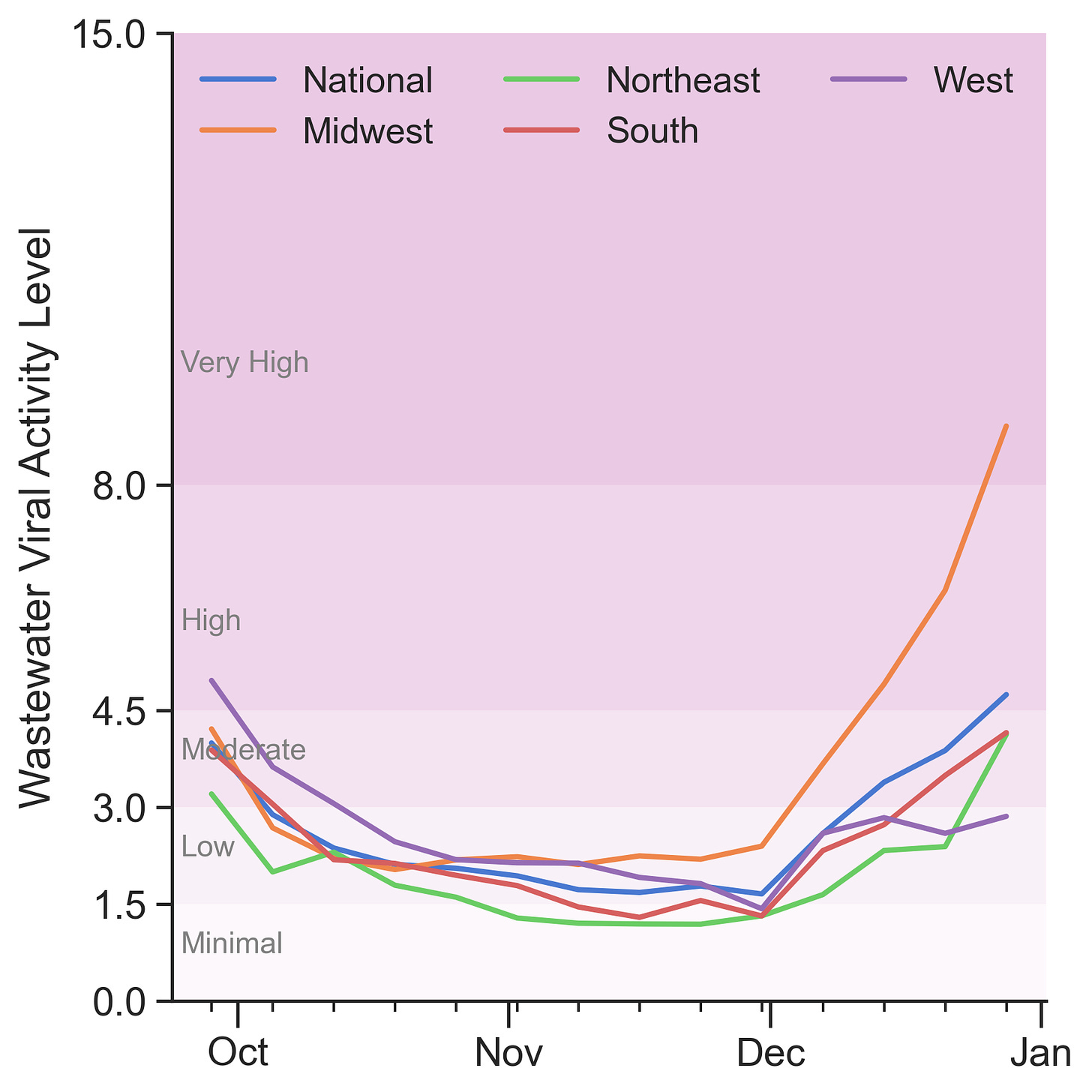
Covid-19 is picking up. Wastewater activity is high nationally, but with a fair amount of regional variation, ranging from low activity in the West to very high activity in the Midwest. Midwestern wastewater activity is about double that in the South and Northeast, and a little over triple that in the West.
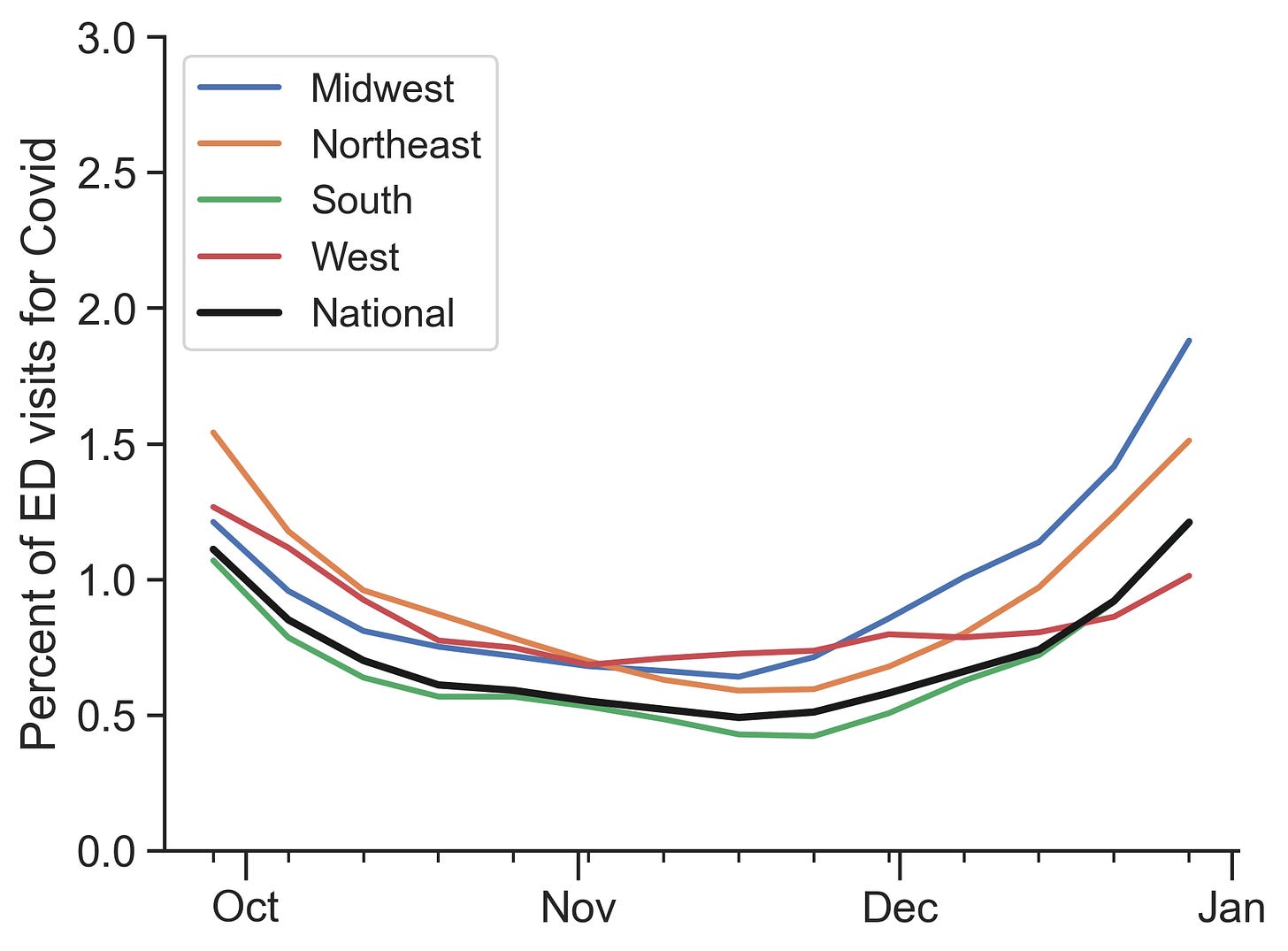
Severe illness is also rising, though it remains fairly low at a national level. Emergency department visits are on an increasing trend, accounting for 1.2% of all ED visits this past week nationally. Hospitalizations have increased to 4.1 hospitalizations per 100,000, up a point from last week.
RSV & Other Bugs
RSV activity is moderate for most of the country. The South has the highest ED visit percentages nationally, with several states exceeding 2% of visits, while also reporting substantial hospitalization rates between 1.2 and 3.0 per 100,000 population. The Midwest and Northeast have moderate activity, and the Northeast reporting some of the highest hospitalization rates despite relatively lower ED visit percentages. Overall, while RSV activity remains lower than influenza.
Human coronaviruses - a common cause of colds - appear to be close to reaching their typical winter peak.
Other causes of cold- and flu-like symptoms are at lower levels. Human metapneumovirus remains low but has started to slowly increase (it tends to peak around mid-spring). Adenoviruses, parainfluenza, and rhinoviruses/enteroviruses are all on the decline.
Norovirus
Norovirus continues to surge, though the rate of increase does appear to be slowing, suggest we may be coming close to a peak. Test positivity increased to an extremely high 22.6% last week. It is possible that this number is a bit inflated given that the number of tests was substantially lower last week than in prior weeks - but even if we assume it is a few points off the mark, this is still extremely high.
Food recalls
The following foods are being recalled because they are contaminated. Please check your cupboards and throw out any of these items:
New:
Wicklow Gold Cheddar Cheeses (more info)
Blue Ridge Beef Kitten mix [for Cats] (more info). While not for human consumption, humans may be infected with Salmonella if they do not adequately wash their hands or contaminated surfaces after handling the product.
Marketside Broccoli Florets (more info)
Previously reported:
Connie’s Thin Crust Cheese Frozen Pizzas (more info)
Daily Veggies Enoki Mushrooms (more info)
Sprouts Markers Market Gyro Family Kit (more info)
MadeGood Granola Bars (various flavors and varieties) (more info)
Blue Ridge Beef log Puppy Mix [for Dogs] (more info)
If you have food allergies, you may wish to review these FDA safety alerts and USDA alerts for foods with undeclared allergens.
In other news
A study published in JAMA Network Open found that influenza vaccination was over 50% effective in preventing emergency department visits and hospitalizations among nearly 16,000 U.S. children during five flu seasons from 2015 to 2020. Vaccine effectiveness was slightly higher among younger children (6 months to 8 years) than older ones, with the highest protection against influenza H1N1 and influenza B strains. Despite the benefits, vaccination coverage in children remains below the U.S. Healthy People 2030 goal of 70% and has declined in recent years.
The Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) has allocated $306 million to bolster the nation’s preparedness for H5N1 avian flu. The funding includes $183 million for regional, state, and local programs to enhance hospital readiness and emerging-pathogen training, $111 million for the CDC to improve virus monitoring and diagnostic test production, and $11 million for NIH research on countermeasures.
Get detailed, state-specific public health updates with regional editions—available to paid subscribers. Stay informed where it matters most to you!















.jpg)
No comments:
Post a Comment